Hysteroscopy
Hysteroscopy
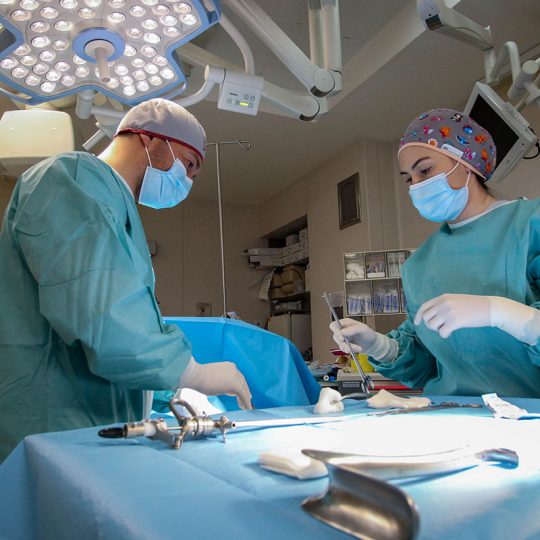
Hysteroscopy is a gynaecological procedure that involves using a specialised optical device (hysteroscope) to inspect the uterine cavity under direct visual control. The procedure is performed in a specially equipped operating room with specific instruments by a highly qualified gynaecologist under anaesthesia. Hysteroscopy is typically performed in the first days after the end of the menstrual cycle when the uterine lining is thinnest. No special preparation is required from the patient, and no hospital stay is necessary. However, due to the nature of the procedure, prior planning is required.


Common indications for hysteroscopy:
- Abnormal uterine bleeding;
- Increased thickness of the endometrium;
- Suspected polyps or fibroid nodules in the uterine cavity;
- Subfertility or infertility;
- Anatomical uterine defects (septate uterus, bicornuate uterus, etc.);
- Adhesions in the uterine cavity after intrauterine procedures (Asherman’s syndrome);
- Removal of a foreign body from the uterine cavity (IUD, etc.).
Depending on the extent of the intervention, hysteroscopy can be either diagnostic or operative. Diagnostic hysteroscopy involves the examination of the uterine cavity, endometrial lining, and internal openings of the fallopian tubes. If pathology is detected (endometrial polyps, submucosal fibroids, adhesions, hyperplasia, bleeding vessels, residual tissue, etc.), operative hysteroscopy is performed. In such cases, specialised instruments are inserted through the working channels of the hysteroscope to remove problematic areas (polypectomy, myomectomy, adhesiolysis) and collect tissue samples for histological examination.
Gynaecology and Obstetrics Doctors

Prim. D-r Tashe Trpchevski
Consultant Gynaecologist and Sub-Specialist in Reproductive Medicine and Surgery

D-r Hristijan Trpchevski
Specialist Gynaecologist & Obstetrician

D-r Vladimir Popovski
Specialist Gynaecologist & Obstetrician

D-r Blagojce Obednikovski
Specialist Gynaecologist & Obstetrician

D-r Kristinka Pajakovska
Specialist Gynaecologist & Obstetrician

D-r Marija Hristovska
Specialist Gynaecologist & Obstetrician

D-r Vladko Gjorgjievski
Specialist Gynaecologist & Obstetrician

D-r Sotir Ropi
Specialist Gynaecologist & Obstetrician

D-r Aleksandar Jovanovski
Specialist Gynaecologist & Obstetrician

D-r Ana Vangelov
Specialist Gynaecologist & Obstetrician

D-r Sanja Milunovikj
Trainee Specialist Gynaecologist & Obstetrician
Medical-Surgical Nurses

Emilija Srbinoska
Responsible Medical Surgical Nurse

Meri Mihevska
Medical Nurse

Natasha Momiroska
Medical Nurse

Zaneta Veselica-Stefanovska
Medical Nurse

Maja Miloshevska
Medical Nurse

Biljana Dimitrovska
Medical Nurse

Sonja Aleksovska
Medical Nurse

Nikolina Risteska
Medical Nurse
Medical Nurses Midwifes

Merlinda Drala
Responsible nurse, gynecology and obstetrics department

Nadica Neshkovski
Medical Nurse

Jasmina Bozinovska
Medical Nurse

Aleksandra Dimovska
Medical Nurse

Fiona Kelja
Medical Nurse

Irena Talevska
Medical Nurse

Hristina Bumbaroska
Medical Nurse

Martina Karanfilovska
Medical Nurse

Dijana Boshevska
Medical Nurse

Sonja Fuzevska
Medical Nurse

Zaneta Vasilevska
Medical Nurse